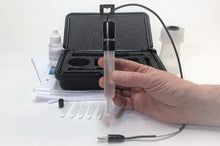
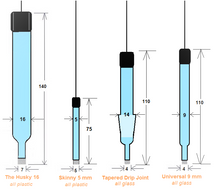
Silver/Silver Sulfate (Ag/SO₄) or the Silver Sulfate Reference Electrode is a Chloride Free, Mercury Free alternative. A new reference electrode for the 21st century. It is truly environmentally green since it does not contain mercury. The Silver Sulfate Electrode is non-hazardous and easy to dispose of. The metal used is pure silver, and the electrolyte is potassium sulfate. The silver-silver sulfate electrode's simplicity and fundamental ruggedness make it a good candidate for many commercial applications where the electrochemical potential must be measured or controlled. We can fabricate your electrode's body to your custom specs.
Ag/Ag₂S0₄ Reference Electrode potential:
-
+0.686 Volts vs. Normal Hydrogen Electrode (NHE)
-
+0.038 Volts vs. Mercury Sulfate Reference Electrode (MSE)
-
+0.440 Volts vs. Saturated Calomel Reference Electrode (SCE)
APPLICATIONS:
- Chloride-free investigations
- Battery testing and maintenance
- Corrosion testing
- Electro-analytical studies
STEPS TO VERIFY VIABILITY OF ELECTRODE:
- Create a ~5mm layer of electrode solution in a beaker
- Place two electrodes of the same type into the pool of solution
- Compare the readings using a volt meter
- If they are within 10 mV of variation, it is good to go!
FEATURES:
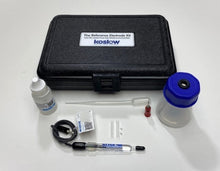
- Carry Case
- Electrode Refill Solution Electrolyte 30 ml
- Laboratory Electrode Storage Bottle
- Pack of 2 Replacement Porous Tips
- 2 Heat Shrinkable Sleeves
- Electrode Filling Pipette
- Absorbent Foam
- Maintenance Manual
- Stable reference
- Internal Filling: silver sulfate and saturated potassium sulfate
- Easily disposable, contains no mercury
- Replaceable frit
HOW IT WORKS:
Electrode potential is stable to plus or minus one millivolt and recovers quickly from small temperature excursions. The electrodes are assembled using pure silver and then anodized to provide the required stability and low noise characteristics.
The junction is Electro-porous KT Glass which serves as the ionically conducting electrical pathway between the inside of the reference electrode and the bulk of your cell. The Electro-porous KT Glass frit is attached to the glass tube by a heat-shrinkable Teflon sleeve. The KT Glass has a low electrical resistance and a modest drip-rate. The electrical resistance of the reference electrode 'frit' is an important factor in determining the stability and speed of your potentiostat's actual use. Remember, when changing KT Glass frits, the heat-shrink tubing should be trimmed flush with the end of the KT Glass frit to prevent the capturing of rogue air bubbles.
The Silver Sulfate Electrode uses a saturated potassium sulfate solution with excess potassium sulfate crystals. These can sometimes be seen on the bottom of the electrode. The extra crystals dissolve into the electrolyte as the ions diffuse through the liquid junction in normal use. This additional buffer of K2SO4 extends the time before the reference cell starts to drift due to the depletion of potassium ions in the electrolyte. Lead-acid batteries investigations and other possible uses of the silver/silver sulfate reference electrode include the determination of individual capacities of positive and negative plates, monitoring individual electrode behavior during deep discharge and cell reversal, optimization charge or discharge parameters by controlling the current such that pre-determined limits of positive or negative half-cell potential are respected, observation of acid concentration differences, for example, due to acid stratification, by measuring diffusion potentials (concentration-cell voltages) and detection of defective cells and defective plate sets, in a string of cells, at the end of their service life.
LEARN MORE: