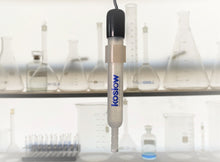
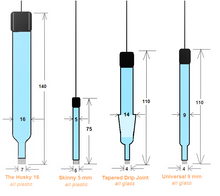
The Silver/ Silver Chloride or simply the Silver Chloride Reference Electrode (Ag/AgCl). The Universal 9 glass body with a banana jack is our standard and is always in stock.
The silver/silver chloride reference electrode is many electrochemists' reference electrode of choice. It is widely used, stable, non-toxic, and robust. The silver-silver chloride electrode's simplicity and fundamental ruggedness make it the right candidate for many commercial applications where the electrochemical potential has to be measured or controlled. It is mainly used with saturated potassium chloride (KCL) electrolytes but can also be filled with lower concentrations, such as 1 M KCL, and even directly in seawater.
- The Silver-Silver Chloride electrode has been shown to possess superior characteristics to that of un-chloridized silver electrodes when recording low-level AC and DC potentials. Chloridized silver electrodes present less low-frequency "noise" than either gold or silver electrodes. The Koslow Silver-Silver Chloride electrodes are pure silver and then chloridized to provide stability and low noise characteristics. The Silver/Silver Chloride potential is approximately (-) 0.199 Volts vs. Normal Hydrogen Electrode (NHE) or -0.047 Volts vs. Saturated Calomel Reference Electrode (SCE). Electrode potential is stable to plus or minus one millivolt and recovers quickly from small temperature excursions.
- The Silver Chloride half cell has applications in electroanalysis, battery testing and maintenance, corrosion testing, electro-analytical studies. Measure half-cell potentials in lead-acid batteries, titration, and many other electrochemical measurements.
- Porous junction tip is made with electroporous KT Glass and is replaceable when damaged or contaminated.
- Excellent ion transfer and low noise
- Traceable ID tags
- Packaged with care in a handy storage carton and includes instructions with SDS.
The Silver/ Silver Chloride Reference Electrode Potential
|
- 197 mV vs. Normal Hydrogen Electrode (NHE) 44 mV vs. Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) |
| - 410 mV vs. Mercury Sulfate Reference Electrode (M.S.E.) |
| - 440 mV vs. Silver / Silver Sulfate |
Learn More:
- More Facts: Koslow reference electrodes use a saturated KCL solution with an excess of KCL crystals. Pale, white crystals can sometimes be seen on the bottom of the electrode. The extra KCL dissolves into the electrolyte as the potassium and chloride ions diffuse out through the liquid junction in regular use. This additional buffer of KCL extends the time before the reference cell starts to drift due to the depletion of chloride ions in the electrolyte.
- Aging: UV light decomposes AgCL to give silver (0) which provides the electrode with a black appearance. LED or fluorescent lights shouldn’t be a problem, but don't store your instruments in direct sunlight. Light protected amber glass storage bottles are recommended to store electrode with frit in KCL filling solution. Saturated solutions of KCL have the advantage that the concentration is reproducible even if the temperature changes (if solid salt is present) and are immune to the effects of water.
- The Electro porous KT Glass tip serves as the ionically conducting an electrical pathway between the inside of the reference electrode and the bulk of your cell. The Electro-porous KT Glass frit (about 1/8" long) is attached to the glass tube by 'heat shrinkable' Teflon sleeve. The Glass has a low electrical resistance (under ten kilo Ohm for the standard filling solutions) and a modest leak rate. The electrical resistance of the reference electrode 'frit' is an essential factor in determining the stability and speed of your potentiostat in actual use. When changing KT Glass frits, the heat-shrink tubing should be trimmed flush with the end of the KT Glass frit to prevent capturing of air bubbles.